Please complete the form below
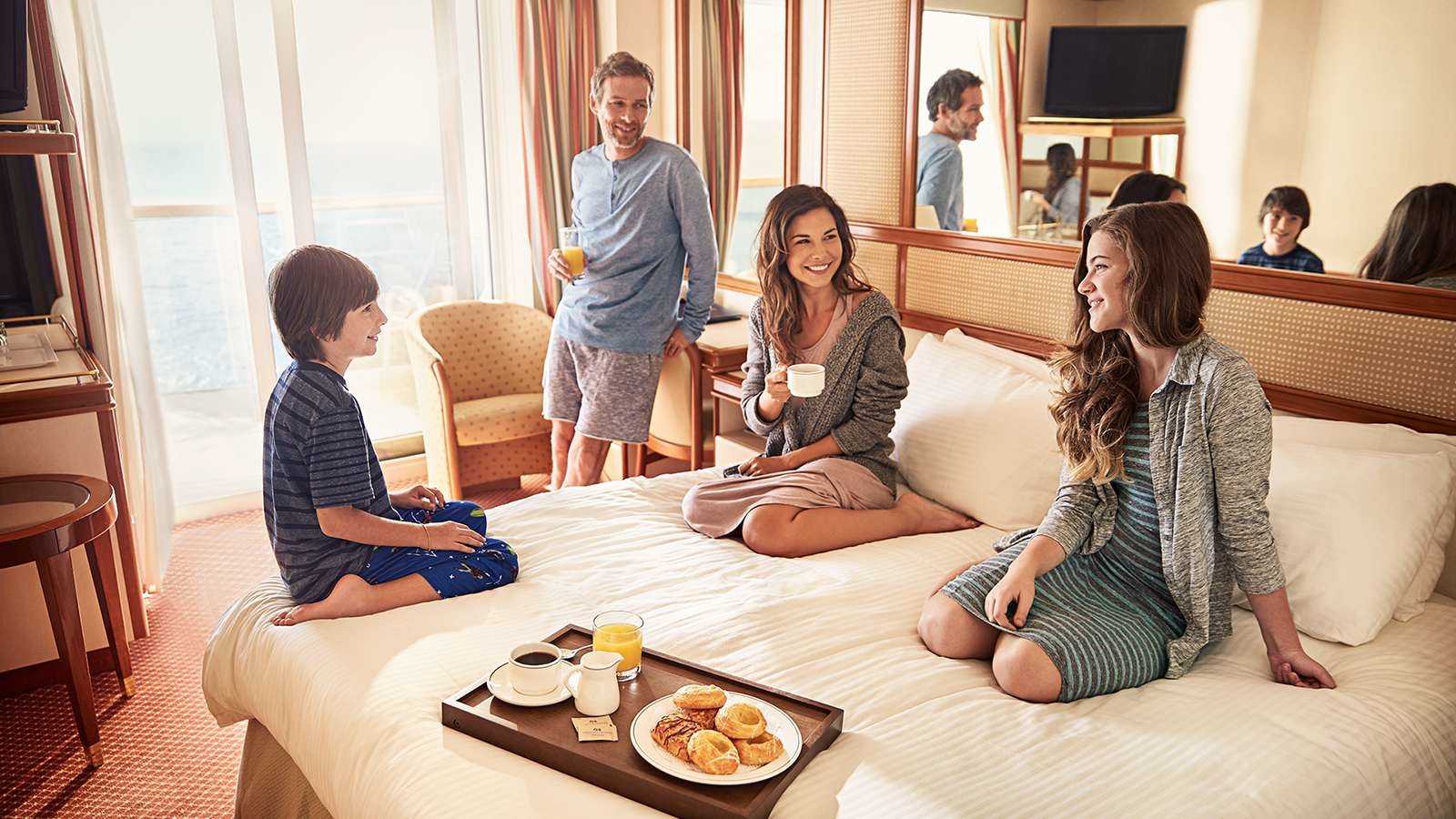


Yokohama and Edo began life as sleepy fishing villages. That changed in the early 17th century after Tokugawa Ieyasu became Shogun. Edo became the center of political power in Japan, a position the city retained even after the restoration of Imperial rule in 1866.
Contemporary Tokyo may be the most astonishing city on earth. It’s a paradoxical mix of ancient tradition and postmodern culture. The Ginza – an international shopping mecca – stands near the serene grounds of the Imperial Palace, and the hyper-speed of 21st century consumerism is mysteriously reconciled with the elegance and serenity of traditional culture. Tokyo provides the traveler with a dizzying experience.
With the Meiji Restoration of 1868, Edo was renamed Tokyo, the “Eastern Capital,” to distinguish it from the old imperial capital at Kyoto, the “Western Capital.”
For most travelers, Nagasaki is a symbol of the horror and the inhumanity of war. An estimated 75,000 people perished in 1945 when the city became the second target of a nuclear attack. Today, Nagasaki’s Peace Park and Atomic Bomb Museum draw visitors from around the world.
But this beautiful city on Kyushu offers other sights. Often described as the San Francisco of Japan, the city occupies verdant hills surrounded by a deep-water bay. For three centuries, Nagasaki was Japan’s sole window on the world. The city is also celebrated as the setting for Puccini’s opera “Madame Butterfly.”
The second largest city in South Korea, Busan is your gateway to a fascinating land whose culture is a unique amalgam of old and new. Modern high-rise towers dwarf ancient Buddhist temples. The city’s bustling business district offers a stark contrast to the serene grounds of Yongdusan Park. In short, Busan is a microcosm of South Korea, a nation whose startling economic success often obscures one of Asia’s most sophisticated and venerable cultures.
Busan was the scene of bitter fighting during the Korean War. The United Nations Memorial Cemetery marks the final resting place for the troops from 16 nations who gave their lives during the conflict.
Wedged between sea, sky and mountains, this small fishing port has been esteemed for centuries for its superb seafood. Here, the Sea of Japan yields up both crab and hon-maguro, the prized Bluefin tuna esteemed by gourmets around the world. Sakaiminato is also your gateway to a very ancient region of Honshu. West of the city lies Izumo-taisha, one of the oldest and holiest shrines in Shinto. This area is dotted with burial mounds from Japan’s Bronze Age. The town of Matsue boasts the celebrated “Black Castle,” a six-story, black-walled castle that home to a clan of the mighty Tokugawa dynasty that ruled Japan for over 250 years. And to the east rises the great snow-capped summit of Mt. Daisen, considered one of the four most scenic mountains in all Japan.
Maizuru is a city in south-central Japan. The Goro Sky Tower has panoramic views over the islands of Maizuru Bay. Maizuru Park contains the ruins of Tanabe Castle, and is known for spring cherry blossoms. East, Brick Park is a group of Meiji-era warehouses, now home to the World Brick Museum.
Kanazawa, which means “marsh of gold,” draws its name from an old legend in which a Japanese peasant, digging for potatoes, found flakes of gold in the ground. Today, gold leaf is a major art form synonymous with the city, and even has a designated museum. A City of Crafts and Folk Art, Kanazawa is also known for its intricate kaga-nui embroidery and delicate kutani porcelain, among other handicrafts, making it a shopper’s paradise! There’s also no shortage of history in this coastal city. Once boasting geisha houses and a labyrinthine samurai village, the city was built around Kanazawa Castle. Fire destroyed all but a few small 16th-century castle structures – namely the elegant Ishikawa Gate and some watchtowers that have become a focus of many a photograph today. Just outside the castle park blooms the enchanting Kenroku-en Garden, one of the Three Great Gardens of Japan, and the home of the country’s oldest fountain.
Sakatais a medium-sized city in Yamagata Prefecture. Sakata is located in the fertile Shonai Plain that is known for its high-quality rice. The city grew as an important stop along the coastal shipping route that connected Hokkaido with Osaka via ports along the Sea of Japan and Seto Inland Sea during the Edo Period.
A local merchant family, the Honma clan, came to dominate trade in the city and accrued a vast fortune that made them wealthier than some of the country’s feudal lords. Due to their power and influence, the clan developed close ties with the local lords and had a number of lavish buildings built. Some of these buildings still stand today along with museums and other attractions.
Since 1889, the old port of Hakata has been part of Fukuoka city, the major commercial center of Northern Kyushu. This region is perhaps the oldest settled area in Japan, and for centuries Hakata served as Japan’s cultural and commercial gateway with China and Korean. The twin cities played another major role in Japanese history – it was here that Kublai Khan launched his two invasions of Japan in the 13th century. Two anchor stones from the great Mongol fleet destroyed by the famous typhoon or Kamikaze are still on display at Hakata’s 8th century Kushida Shrine. Beyond the hustle and bustle of today’s modern metropolis, visitor will still discover and enjoy the serenity of ancient shrines, superb formal gardens, and a duo of fascinating museums.
When Hakata and Fukuoka merged in 1889, the combined metropolis was to be named Hakata. Until a group of disaffected samurai from Fukuoka – an important castle town in feudal times – intervened to ensure the new city’s name honored their old home.
A pretty prefecture located on the northeastern coast of Honshu, Japan’s main island, Miyako, Iwate, is situated along the Pacific coast surrounded by stunning scenery of Sanriku Fukko National Park and a sandy coastline defined by dramatic rock formations carved by the pounding surf. This iconic landscape invokes images of the ‘Pure Land,’ a Buddhist concept of paradise, and is best appreciated from the deck of a cruise boat on the waters of Jodogahama. The city’s natural wonders are woven within its cultural highlights, and a visit to Kamaishi Daikannon Statue, a towering statue of the Buddhist ‘Goddess of Mercy,’ showcases sparkling Kamaishi Bay, while the historic Rokando Cave, is home to “the waterfall of the heavenly cave,” an underground cascade. No visit to Miyako’s shores would be complete without paying reverence to the tragedy that occurred on March 11, 2011, when a powerful earthquake triggered a devastating 17-meterhigh tsunami. The Taro Kanko Hotel Tsunami Remains is a testament to the power of the community’s resiliency and serves as commemorative site, an important destination for those lucky enough to visit the island as it blooms with renewal.
Hitachinaka is a city located in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 July 2020, the city had an estimated population of 154,663 in 64,900 households and a population density of 1547 persons per km². The percentage of the population aged over 65 was 26.1%. The total area of the city is 99.96 square kilometres.
Yokohama and Edo began life as sleepy fishing villages. That changed in the early 17th century after Tokugawa Ieyasu became Shogun. Edo became the center of political power in Japan, a position the city retained even after the restoration of Imperial rule in 1866.
Contemporary Tokyo may be the most astonishing city on earth. It’s a paradoxical mix of ancient tradition and postmodern culture. The Ginza – an international shopping mecca – stands near the serene grounds of the Imperial Palace, and the hyper-speed of 21st century consumerism is mysteriously reconciled with the elegance and serenity of traditional culture. Tokyo provides the traveler with a dizzying experience.
With the Meiji Restoration of 1868, Edo was renamed Tokyo, the “Eastern Capital,” to distinguish it from the old imperial capital at Kyoto, the “Western Capital.”
For most travelers, Nagasaki is a symbol of the horror and the inhumanity of war. An estimated 75,000 people perished in 1945 when the city became the second target of a nuclear attack. Today, Nagasaki’s Peace Park and Atomic Bomb Museum draw visitors from around the world.
But this beautiful city on Kyushu offers other sights. Often described as the San Francisco of Japan, the city occupies verdant hills surrounded by a deep-water bay. For three centuries, Nagasaki was Japan’s sole window on the world. The city is also celebrated as the setting for Puccini’s opera “Madame Butterfly.”
Jeju-do lying off the south coast of Korea is the warmest and wettest place in the entire country. The island is at its most beautiful in spring when the azalea blooms in a riot of delicate colours and the wooded areas display the most fascinating shades of green. In Jeju the seasons determine the changing hues of color through the island. In the autumn the color that dominates is brown and orange due to the falling leaves, in summer the aqua blue waters of the sea and golden beaches take over as in spring the brilliant yellow flowers cover the landscape.
Jeju Island, also known as the “Island of the Gods,” is a popular vacation spot for Koreans and many Japanese. It remains one of the top honeymoon destinations for Korean newlyweds. The island’s mixture of volcanic rock, frequent rains, and temperate climate, make it very similar to the Hawaiian Islands in the U.S. The island offers visitors a wide range of activities: hiking on Halla-san (South Korea’s highest peak), catching sunrises and sunsets over the ocean, viewing majestic waterfalls, riding horses, or just lying around on the sandy beaches.
One of the most outstanding features of the island is a regular maze of tunnels, caves and pillars formed by the cooling of lava flows from ancient volcanoes. Jeju-do is basically an island composed of extinct volcanoes formed by volcanic matter such as basalt and trachyte and layered with sedimentary rock. It still has a volcano- an extinct one, called Mt Hallasan, which, at 1950 m also doubles up as the island’s main mountain. The main city on the island is Jeju City, the main base for trekking, sightseeing and exploring the rest of the island.
In 1880, the first railroad line on the island of Hokkaido connected Sapporo, the prefectural capital, with the important port city of Otaru. Indeed, for most of the 19th and much of the 20th centuries, Otaru outshone Sapporo in importance. The city was home to a thriving herring fleet. Ships regularly plied the waters between the port and the then Japanese island of Sakhalin. Coal was mined in the hills, and Otaru even won a reputation for producing fine music boxes. It was the island’s industrial heart. Closure of coal mine in Hokkaido and downturn in demand of coal initiated a long decline that lasted into the 1950s. But Otaru survived – and has thrived. Japanese travelers discovered the city, drawn to its winter sports, its fine sushi, and its historic architecture. Otaru seemed like a portrait frozen in time. Today, international travelers have flocked to experience Otaru’s charms – including the scenic beauty of Hokkaido’s rugged west coast and its nearby national parks.
The vast wealth accumulated by Otaru’s herring tycoons is displayed at their so-called “Herring Mansions.” One, the Nishin Goten, built in 1897, amply illustrates the state of 19th century society: the sumptuous ground floor housed the family while as many as 120 workers lived in squalor upstairs.
The capital of the Aomori Prefecture in northern Japan, Aomori derives much of its beauty from the apple orchards and cherry blossoms that encompass its landscape and the snow-covered Hakkoda Mountains that look on from a distance. Throughout its history, the city has been stricken with misfortune time and time again – in 1910, a fire destroyed Aomori, and during World War II, the city was left in ruins following an air raid – yet it always prevails.
Aomori is cherished by many who believe a local legend that the grave of Jesus Christ lies within the southern part of Aomori prefecture. However, Aomori is perhaps best known for its renowned Nebuta Festival, an elaborate yearly event in which participants illuminate giant paper representations of samurai warriors, animals, and popular cartoon characters while parading them through the streets.
Located on the southwest part of the island of Hokkaido, Muroran is a major industrial center and your gateway to Hokkaido’s natural beauty. This island’s unhurried pace is a welcome contrast from the hustle and bustle of Honshu and Kyushu. Relatively uncrowded and unspoiled, Hokkaido offers dramatic landscapes ranging from dense forests and hot springs to active volcanoes and calm lakes nestled in calderas.
Yokohama and Edo began life as sleepy fishing villages. That changed in the early 17th century after Tokugawa Ieyasu became Shogun. Edo became the center of political power in Japan, a position the city retained even after the restoration of Imperial rule in 1866.
Contemporary Tokyo may be the most astonishing city on earth. It’s a paradoxical mix of ancient tradition and postmodern culture. The Ginza – an international shopping mecca – stands near the serene grounds of the Imperial Palace, and the hyper-speed of 21st century consumerism is mysteriously reconciled with the elegance and serenity of traditional culture. Tokyo provides the traveler with a dizzying experience.
With the Meiji Restoration of 1868, Edo was renamed Tokyo, the “Eastern Capital,” to distinguish it from the old imperial capital at Kyoto, the “Western Capital.”

Finding the latest prices
Please complete the form below